List of countries and dependencies in the world ranked by life expectancy at birth, both sexes, males and females World Population Life Expectancy with historical chart Implications of Low Life Expectancy In Developing Countries (1) Loss of productive workforce In many parts of African continent, life expectancy continued to decrease For instance, Botswana people use to live up to 60 years old but now averaging at 40 years of age South Africa which is relatively the performer among African peers, does not Life expectancy in the US and peer countries has generally been increasing from While life expectancy in the United States decreased from its alltime high of 7 years after 14 (driven by increase in overdose deaths), life expectancy increased in 18 and 19 and was back up to 7 years in 19 Life expectancy increased in most comparable countries
1
How does low life expectancy affect a country
How does low life expectancy affect a country- Developing Country is a country which has a slow rate of industrialization and low per capita income Unemployment and Poverty Low High Rates Infant mortality rate, death rate and birth rate is low while the life expectancy rate is high High infant mortality rate, death rate and birth rate, along with low life expectancy rate LivingTwo possible solutions for low life expectancy in developing countries Explain what causes people die at young age such as malnutrition, lack of education and poor health care system Possible solutions Educate people from developing countries, improve health services and provide nutritional food Disaster such as drought, flood causes unable




Global Age Sex Specific Fertility Mortality Healthy Life Expectancy Hale And Population Estimates In 4 Countries And Territories 1950 19 A Comprehensive Demographic Analysis For The Global Burden Of Disease Study 19 The Lancet
A low life expectancy can be defined as a belowaverage age a person might reach on average when he or she is born for every respective date Especially in poor developing countries, life expectancy is quite low compared to rich industrialized countries In addition, the life expectancy at birth variable that mostly used in related literature as a proxy of health status and wellbeing, it is used in our study as a proxy of SDG3 In this study, we investigated the role of globalization and democracy in life expectancy in 16 lowincome countries Covid19impactpredictionindevelopingcountries By analaysing a data from different provinces of China, I predity how significant Covid19's imact would be in developing countries with low income and low life expectancy This project is done in spring of in early stages of covid19 pandemic
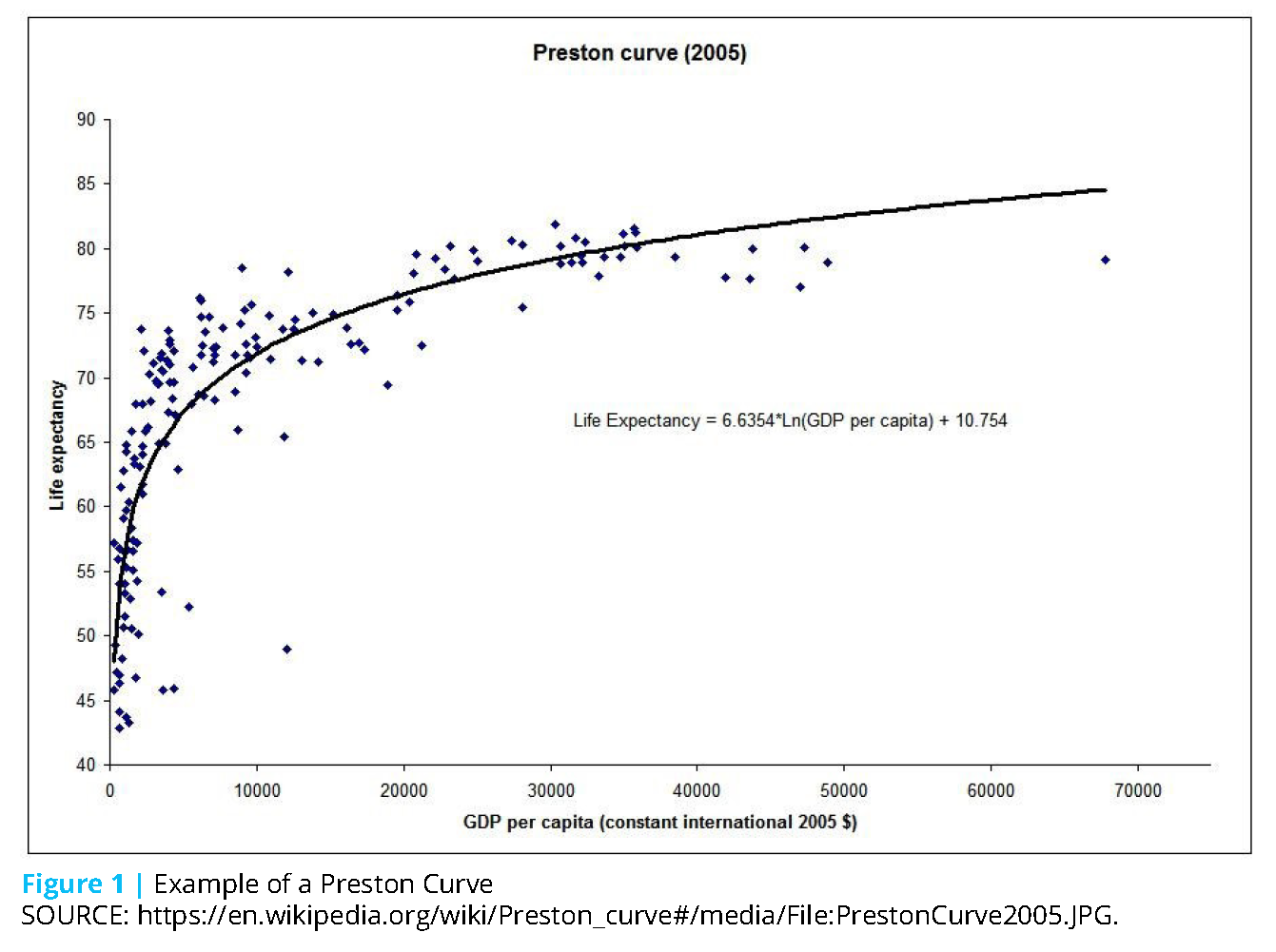
Research on international inequalities in life expectancy has traditionally focused on overall mortality, 3, 6, 8 but there are well known gender differences in mortality trends across countries, 9 – 11 and withincountry inequalities in life expectancy also vary by gender 12 – 14 This suggests that the pattern of international inequality in life expectancy could differ by gender, but noLife Expectancy at birth is widely accepted as a useful indicator of the health status of a country's population and beyond that, is extensively used by international agencies as a general indicator of national development New Orthodox economists regard longevity as one of the key functioning's for economic development (UNDP 1990) Over the past few decades', developing countriesData analyses reveal that the lowest life expectancy is 4178 years, while the highest is 7984 years Lowincome DC have low performance in terms of life expectancy at birth While highincome DC recorded strong performances Hence the existence of a positive correlation between life expectancy at birth and GNI per capita (Figure 1) Figure1
Life expectancy varies by 34 years between countries In lowincome countries, the average life expectancy is 62 years, while in highincome countries, it is 81 years A child born in Sierra Leone can expect to live for 50 years while a child born in Japan can expect to live 84 yearsAnswer (1 of 2) Because they have much much higher infant and childhood mortality rates, often because of very poor nutrition, mixed with poor water quality and a high incidence of diarrheal disease They also often have a higher amount of fighting, andLow Life Expectancy in Developing Country of Nigeria 666 Words 3 Pages Life expectancy estimates the equivalent years in full health that a person can expect to live on the basis of the current mortality rates and prevalence distribution of health states in the population (WHO 12)




Recent Trends And Increasing Differences In Life Expectancy Present Opportunities For Multidisciplinary Research On Aging Nature Aging




Future Life Expectancy In 35 Industrialised Countries Projections With A Bayesian Model Ensemble The Lancet
While in general a country's life expectancy increases with national income, some countries "punch above their weight", while some "punch below their weight" – achieving higher or lower life expectancy than would be predicted by their per capita income Discovering which conditions or policies contribute to this outcome is critical to improving population health globally This statistic shows the average life expectancy in developed countries vs developing countries In developed countries, the life expectancy was years for females and 76 years for males in 18Methodology The life expectancy is shown separately for males, and for females, as well as a combined figure Several nonsovereign entities and territories are also included in this listThe figures reflect the quality of healthcare in the countries listed as well as other factors including ongoing wars, obesity, and HIV infections From the beginning of the current century there is a
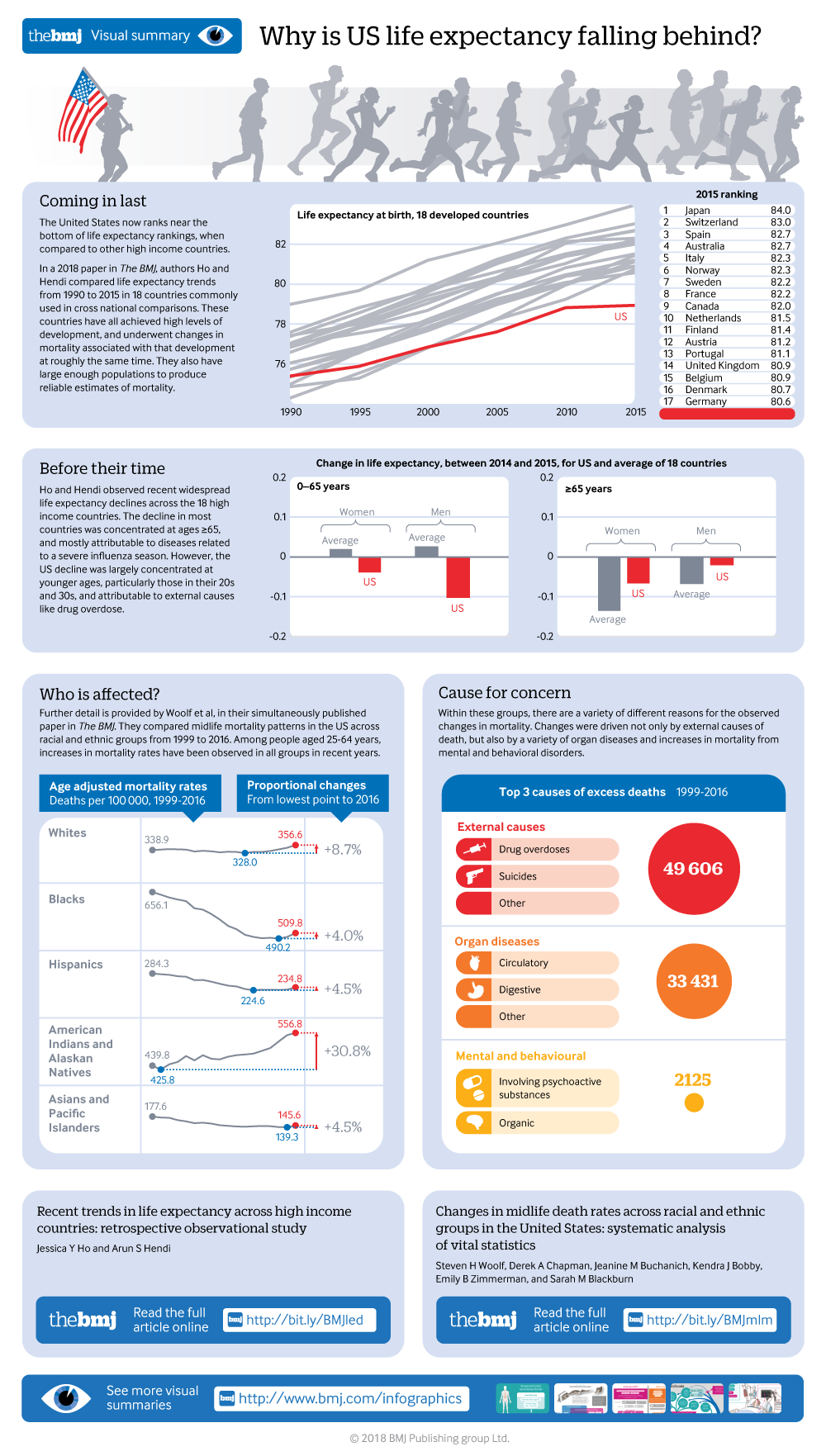



Recent Trends In Life Expectancy Across High Income Countries Retrospective Observational Study The Bmj
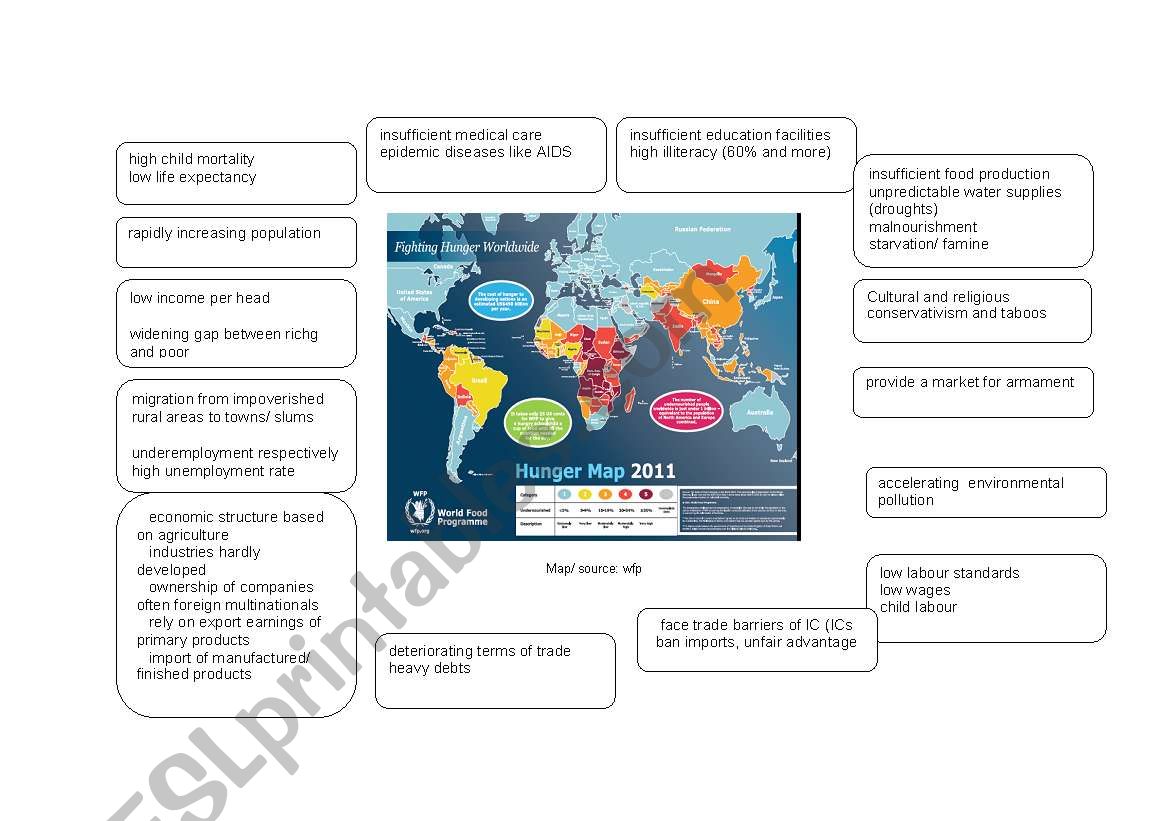



Problems Of Developing Countries Mindmap Esl Worksheet By Klau1994
Life expectancy in the United States fares poorly in international comparisons, terrorism and low level of education are the factors responsible for the low life expectancy of developing countries MADISON, diarrhea, France) Frank reversals occurring mostly in developing countries where the HIV epidemic led to a significant decline in life Nigeria has one of the lowest life expectancy rates in the world;Husain Life Expectancy in Developing Countries 163 Research on life expectancy, and infant or childhood mortality in developing countries has been extended in various directions recently Many of the recent analyses have emphasized the importance of socioeconomic and other factors in explaining differences in mortality
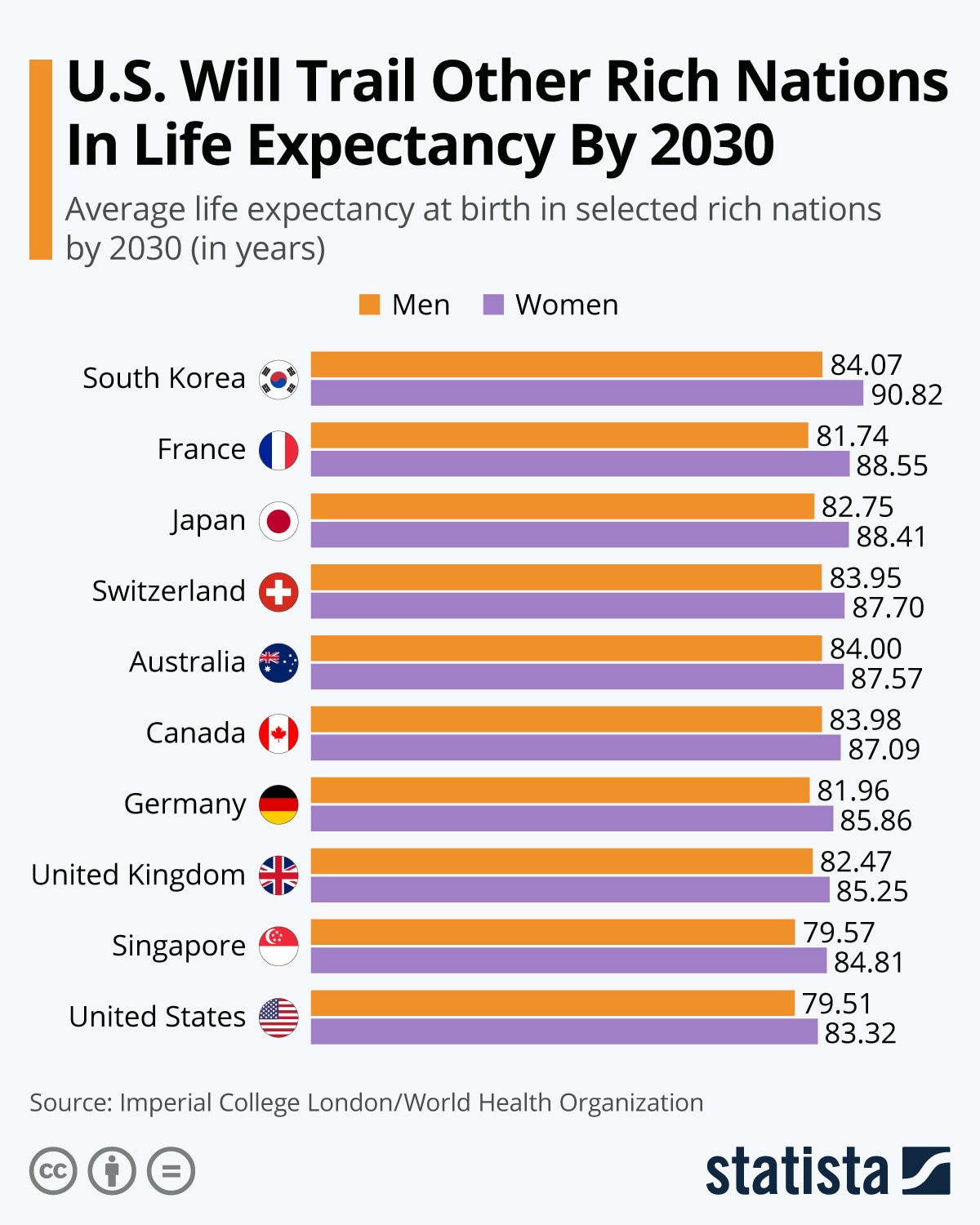



Which Country Has The Highest Life Expectancy World Economic Forum
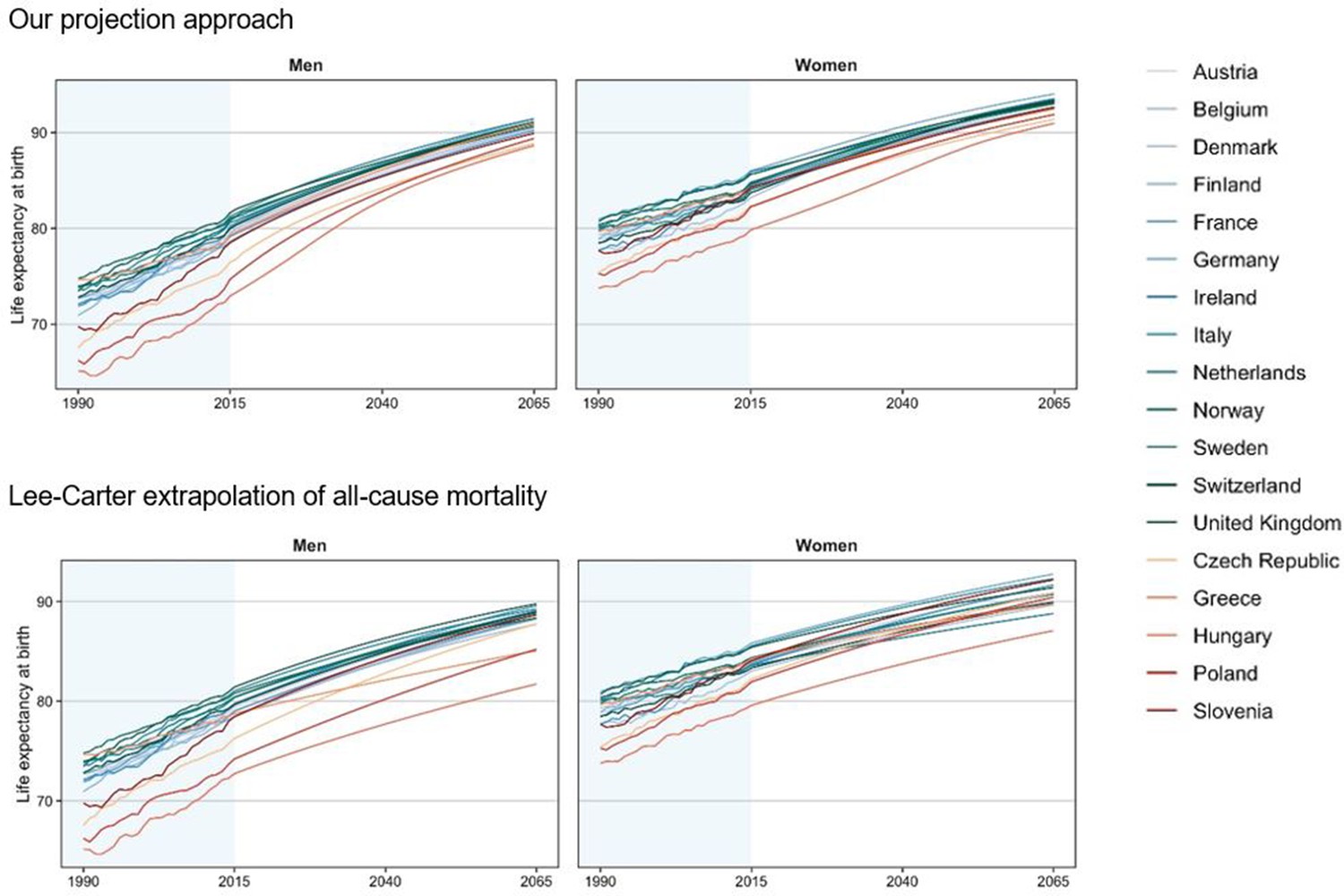



Future Life Expectancy In Europe Taking Into Account The Impact Of Smoking Obesity And Alcohol Elife
Estonia, which has a high expectancy for Eastern Europe, would rank quite low in Western Europe Of the lowest ranked countries, all of Countries By Life Expectancy When children are born, their parents or society expect them to live as long as possible However, the number of years a person can live depends on their exposure to risks, accidents, diseases, birth events (complications at birth), and the general life expectancy of the society they are born into The extension of life expectancy has always been a primary interest of medical research as well as an indicator of national public health profiles Life expectancy has exhibited patterns of continuous growth over time, but it has also demonstrated persistently high variability between countries over the past halfcentury 2, 3As of 08, the gap in life expectancy
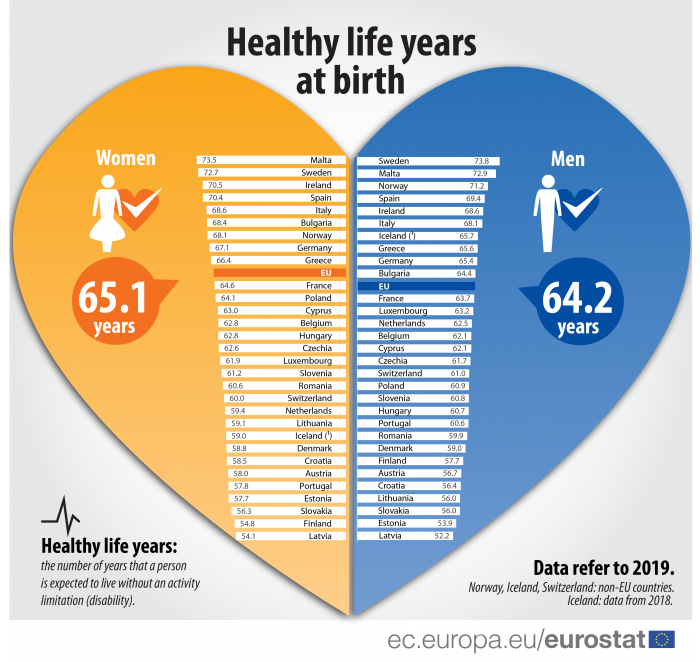



Healthy Life Years Statistics Statistics Explained




Life In Developing Countries Continues To Improve The Economist
This video compares the life expectancy of all countries/regions The median age of each country is also plotted Note that some regions included are not couThis sector of the city exhibited a seven years lower life expectancy than the remainder of the city However, Rogers and Wofford (19) found the opposite result; FC/PM501 Skills for Study 1 Essay Investigate two possible solutions to low life expectancy in the developing world Word Count757 Tutor Scott Benson City Student number Date Life expectancy is one of the most utilized measurements in the demographics of a country
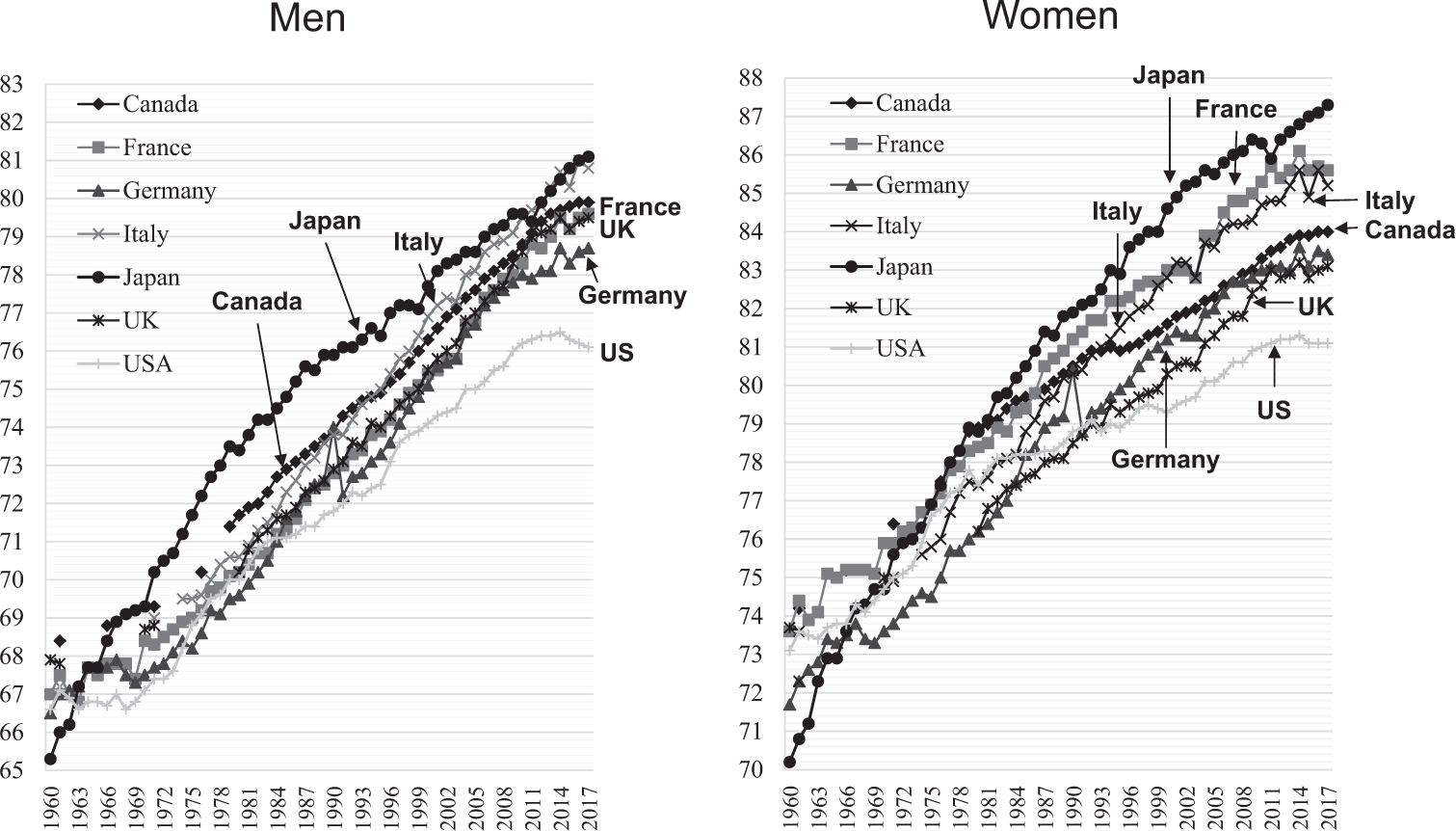



Why Has Japan Become The World S Most Long Lived Country Insights From A Food And Nutrition Perspective European Journal Of Clinical Nutrition




Sustaining Long Run Growth And Macroeconomic Stability In Low Income Countries The Role Of Structural Transformation And Diversification Background Notes In Policy Papers Volume 14 Issue 039 14
Healthy life expectancy (HALE) at birth is an important indicator of health status and quality of life of a country's population However, little is known about the determinants of HALE as yet globally or even countryspecific level Thus, we examined the factors that are associated with HALE at birth in low and lowermiddleincome countries This paper investigates the effect of the socioeconomic development on life expectancy at birth as an indicator of mortality or longevity in five EU accession candidate countries (Macedonia, Serbia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, and Albania) Using aggregate time series pool data on an annual level from UN and World Bank databases for the periodLife expectancy The average life expectancy of a country usually draws a conclusion to medical and hygienic standard The oldest people in the world can be 115 years and even older Most of these records were set in the US, Japan and a few European countries The usual retirement period, is often not more than 1015 years instead
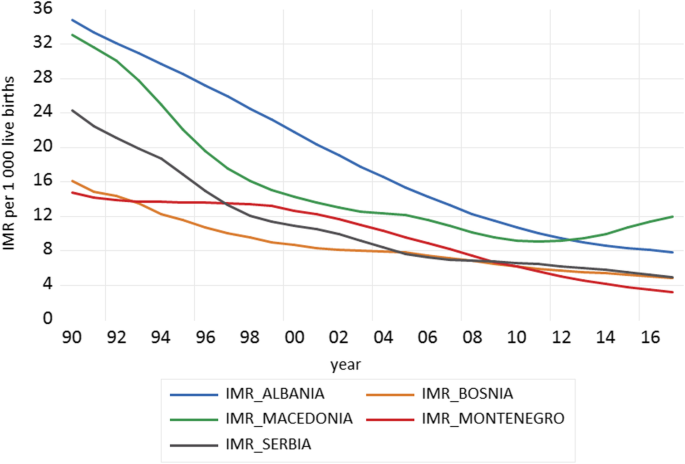



Socioeconomic Development And Life Expectancy Relationship Evidence From The Eu Accession Candidate Countries Genus Full Text
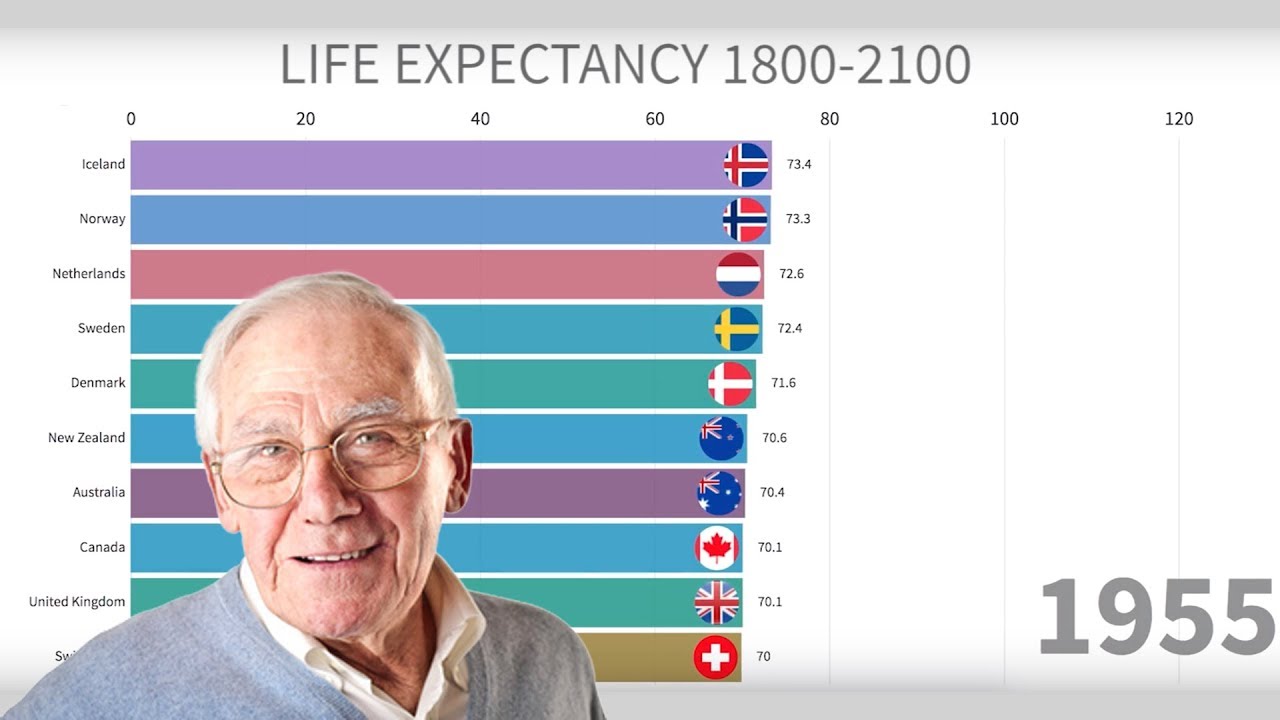



Causes For Low Life Expectancy How To Increase It E C
Examining life expectancy for 95 developing countries they revealed that urbanization was less influential in explaining life expectancy than anticipated, perhaps because of unhealthyAccording to The World Bank, the average worldwide life expectancy at birth was 7033 years in 11, a data research published in 13 World Development Indicators Mortality Humans were expected to live five years longer in 11 than in 1990 However, the low life expectancyDeveloping countries, since they often require only a few doses to deliver and can be delivered by personnel with limited medical training The controversy over intellectual property rights for pharmaceuticals and access to antiretroviral therapies in developing countries has been the subject of much public debate recently



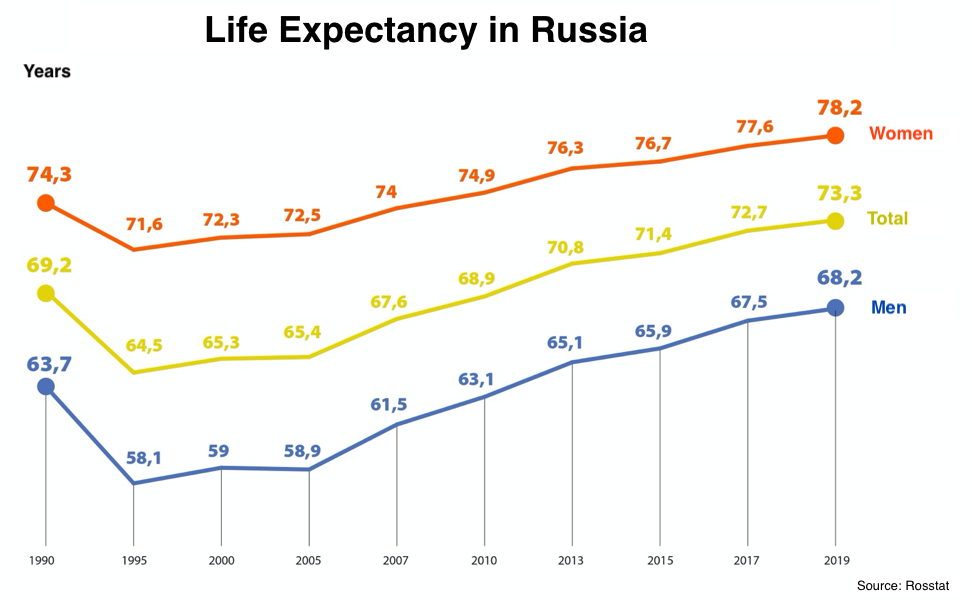
Why Is The Life Expectancy Low In Russia Quora



Life Expectancy Our World In Data
Analysis of the effect of these two groups of factors upon life expectancy, using data for 95 less developed countries, indicates that mortality is primarily influenced by such socioeconomic development measures as urbanization, industrialization, and education, and secondarily by such public health measures as access to safe water, physicians, and adequate nutritionOver the last decades this global inequality decreased No country in the world has a lower life expectancy than the countries with the highest life expectancy in 1800 Many countries that not long ago were suffering from bad health are catching up rapidly Since 1900 the global average life expectancy has more than doubled and is now above 70 The countries with the lowest life expectancy worldwide are all low income or developing countries that lack health care access and treatment that more developed countries



How Did Japan Go From Being A Country With High Fertility Rates And Low Life Expectancy To Low Fertility Rates And High Life Expectancy Quora
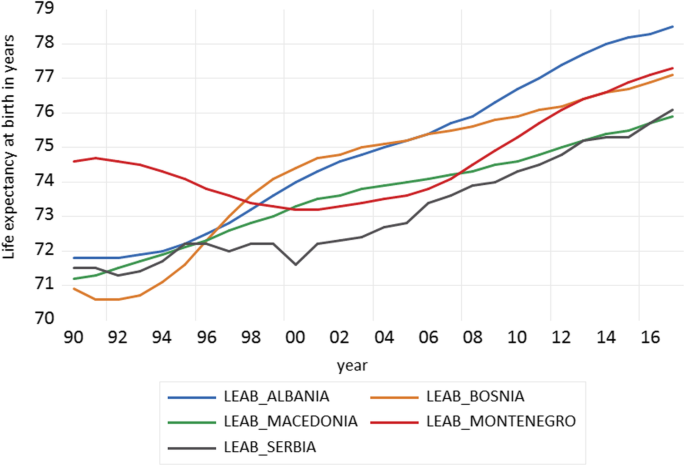



Socioeconomic Development And Life Expectancy Relationship Evidence From The Eu Accession Candidate Countries Genus Full Text
Even countries that have seen an improvement in life expectancy now face a sharp decline China rates as a low mortality developing country, with less than 10 percent of deaths currently occurringA country's economic development may also be reflected in average life expectancy, which indicates the achievement of long and healthy lives and is measured by life expectancy at birthIn 17, the country ranked 214th out of 224 nations The current life expectancy in Nigeria is 538 years, with women living slightly longer than men Though the life expectancy in Nigeria is one of the lowest in the world, it has increased notably in recent decades In 00, the life expectancy in Nigeria was




Future Life Expectancy In 35 Industrialised Countries Projections With A Bayesian Model Ensemble The Lancet
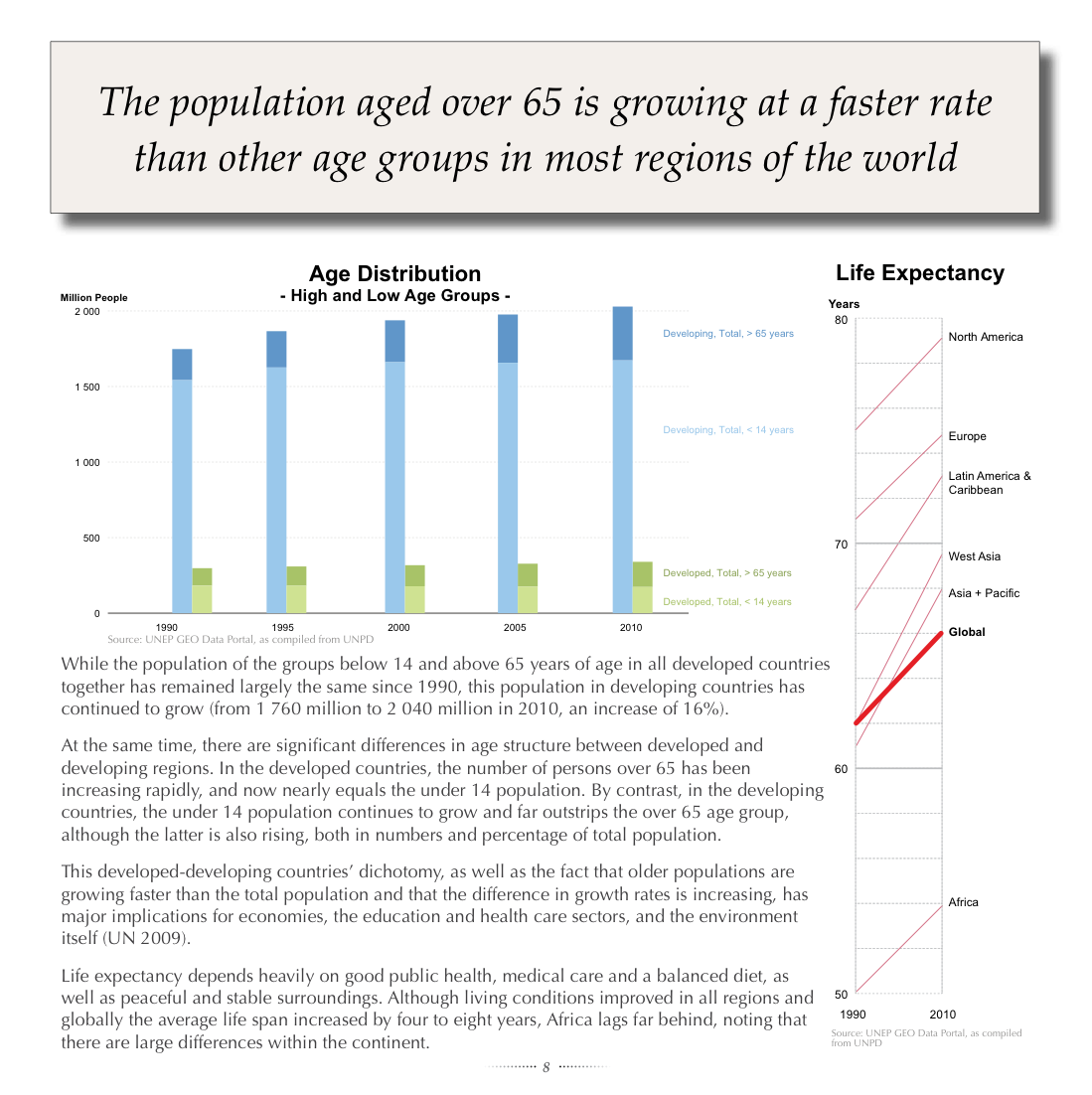



Grid Resource Details
The rst one blames globalization and argues that poverty and as a result of this, low life expectancy derives from the inequality created by globalization itself (Buss 02) The second group mostly focuses on the benets of free trade, capital mobility, and technology transfers (Rao and Vadlamannati 11) The lowincome countries also suer Life disparity is a measure of how much lifespans differ among individuals We define a death as premature if postponing it to a later age would decrease life disparity Results In of the 170 years from 1840 to 09, the country with the highest male life expectancy also had the lowest male life disparity The low life expectancy of poorer Americans is a big part of why the average life expectancy in the US is lower than in other rich countries Kinge et al (19) study the difference between the US and Norway 8 Like the US, Norway is exceptionally rich, but
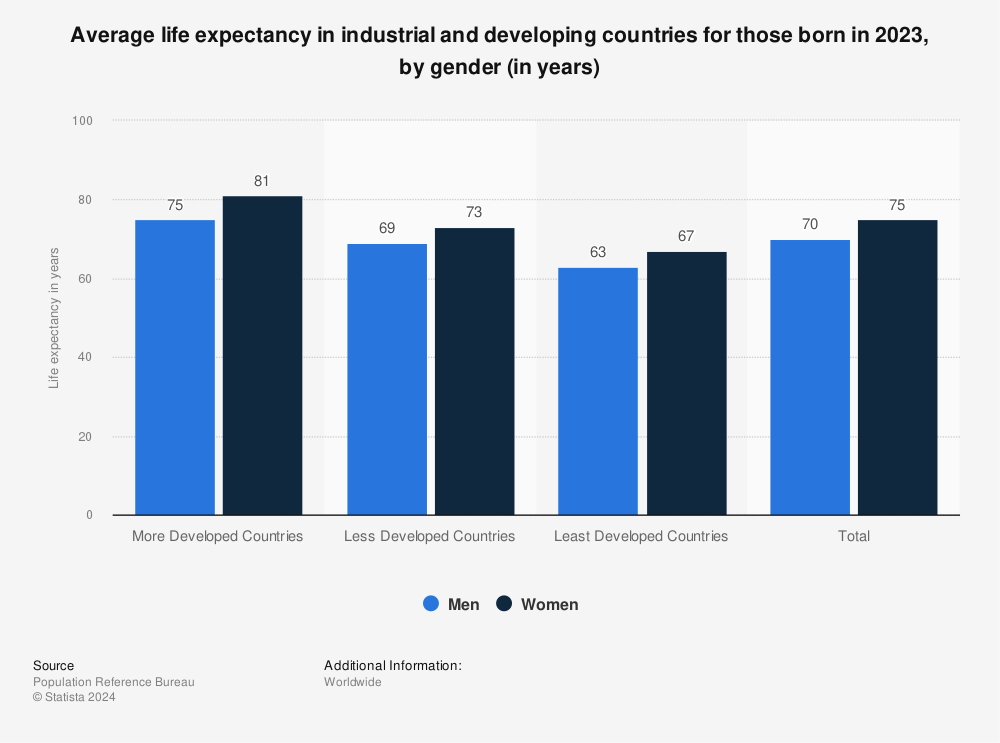



Life Expectancy In Developed And Developing Countries Statista




Zusammenfassung Abitur Global Studies Developing Countries World Trade Docsity
However, because these diseases happen at a much lower rate and tend to develop later in life, life expectancy in lowincome countries continues to rise Since life expectancy is a reliable indicator of health levels in a particular region, The next highest North American country is Costa Rica at 31, then the United States at 35 It's important to note that the life expectancy in Europe varies greatly between Western Europe and Eastern Europe;Low Life Expectancy 560 Words3 Pages World population is facing challenges of low life expectancies in developing countries, overpopulation of people, and a high infant mortality rate due to regulations and a low quality of health Developing countries typically have lower life expectancies due to a lack of nutritious food, safe drinking



Life Expectancy Our World In Data



How Does U S Life Expectancy Compare To Other Countries Peterson Kff Health System Tracker
Increasing number of low life expectancy in developing countries Main problems and consequences in third world Possible solutions Educate people from developing countries, improve health services and provide nutritional food Main body Shortage of food as population is bigger and bigger these days which unbalance between the demand and



Data Highlights 21 Troubling Health Trends Holding Back Progress On Life Expectancy Epi




Pdf Factors Effecting Life Expectancy In Developed And Developing Countries Of The World An Approach To Available Literature



1
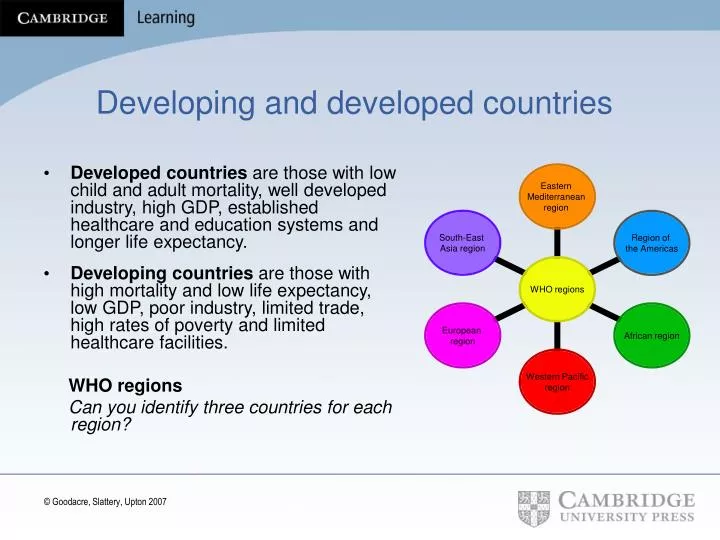



Ppt Developing And Developed Countries Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
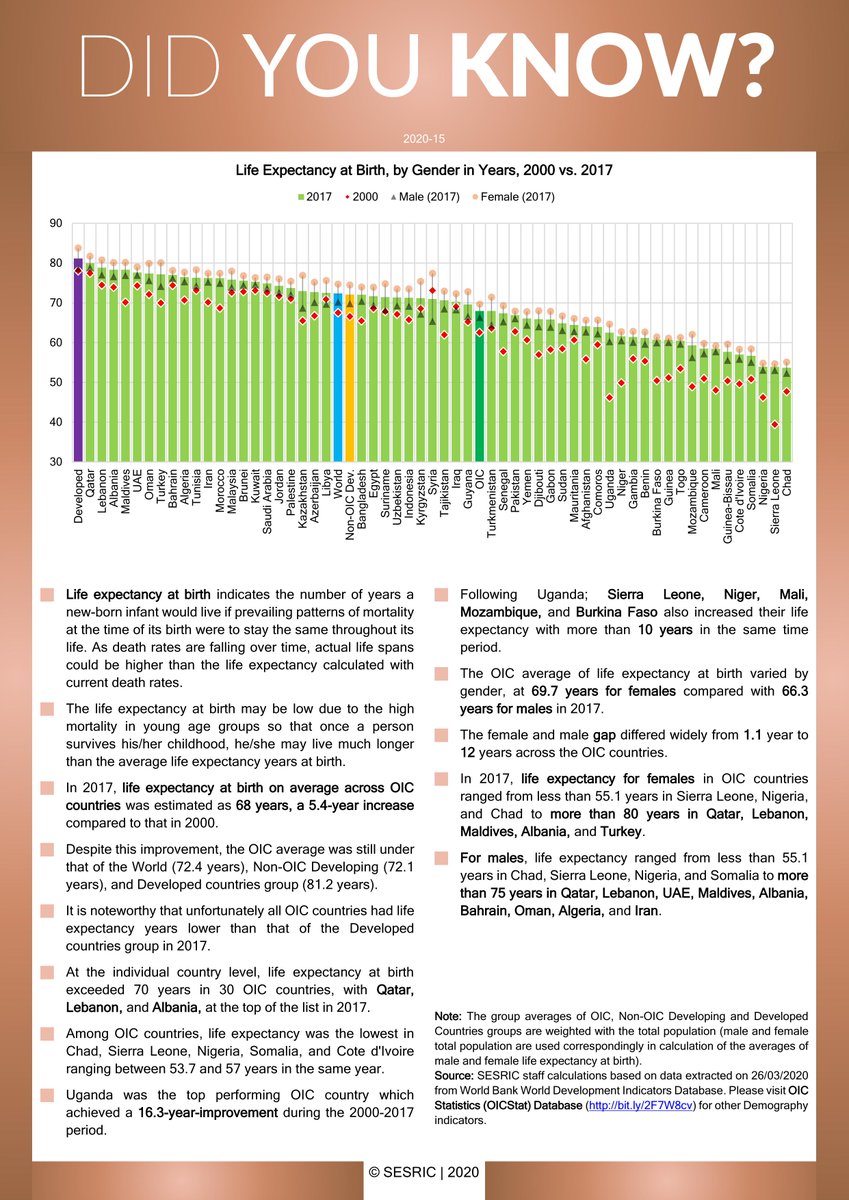



Oic Statcom Didyouknow That Life Expectancy At Birth On Average Across Oic Oci Countries Was Estimated As 68 Years In 17 A 5 4 Year Increase Compared To That In 00 You Can Read



Developed And Developing Nations Sol8 Ppt Download




International Studies What Does It Mean To Be A Citizen Of The World Take A Few Minutes To Brainstorm What Someone Being A Citizen Of The World Ppt Download
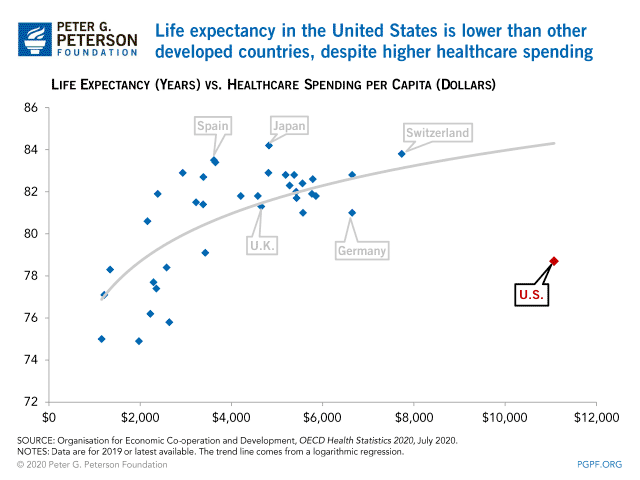



U S Life Expectancy Is Lower Than Other Developed Countries




Global Age Sex Specific Fertility Mortality Healthy Life Expectancy Hale And Population Estimates In 4 Countries And Territories 1950 19 A Comprehensive Demographic Analysis For The Global Burden Of Disease Study 19 The Lancet




Global Health 13 What Do We Need To




Life Expectancy In 35 Industrialized Countries Us Ranks Among The Lowest Fanatic Cook
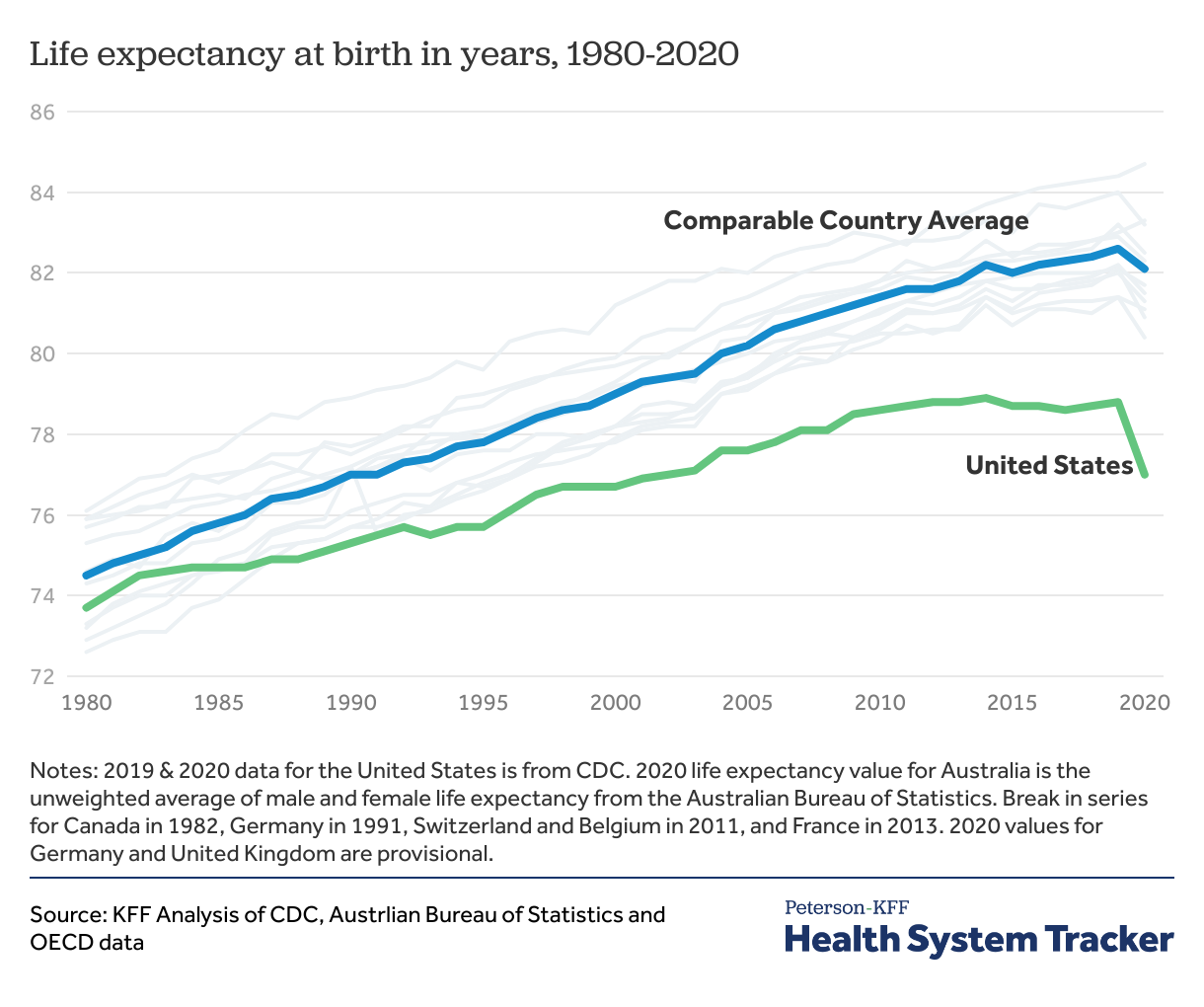



How Does U S Life Expectancy Compare To Other Countries Peterson Kff Health System Tracker



2



Life Expectancy Our World In Data



National Life Tables Life Expectancy In The Uk Office For National Statistics




Countries By Life Expectancy Statisticstimes Com



What Happens If You Combine Life Expectancy And Gdp Into A Single Indicator You Spend More On Health Fp2p



1




What Is Happening To Life Expectancy In England The King S Fund




Projected Global Life Expectancy 2100 Statista




Global Health Chpt 8 Unit 4 Aos 1 Key Knowledge And Key Skills Key Knowledge Characteristics Of Developed And Developing Countries Similarities Ppt Download




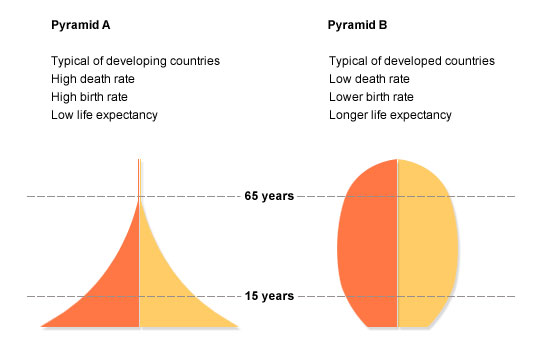
Mdc Ldc Hdi More Developed Countries Less Developed




U S Life Expectancy Fell By A Year In The First Half Of Cdc Report Finds




Life Expectancy Wikipedia




Life Expectancy As A Measure Of Inequality The Hindu Businessline



Life Expectancy Our World In Data
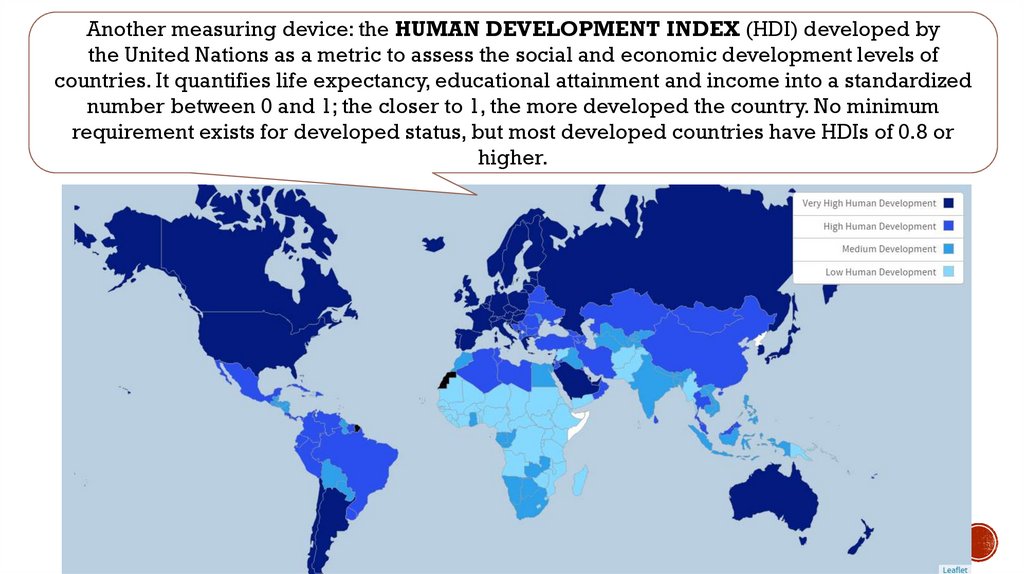



World Economics Meaning Of Development Prezentaciya Onlajn




Comparison With Other Nations 16 Annual Report Ahr




Regional Trajectories In Life Expectancy And Lifespan Variation Persistent Inequality In Two Nordic Welfare States Wilson Population Space And Place Wiley Online Library




The 10 Countries With The Lowest Life Expectancy Borgen



Quality Of Life Or Medicine Hse Researchers Learn The Key To Living Longer Hse University



2




Economic Growth And Life Expectancy Do Wealthier Countries Live Longer Euromonitor Com



Life Expectancy Discrepancies Outcomes And Future Directions Princeton Public Health Review
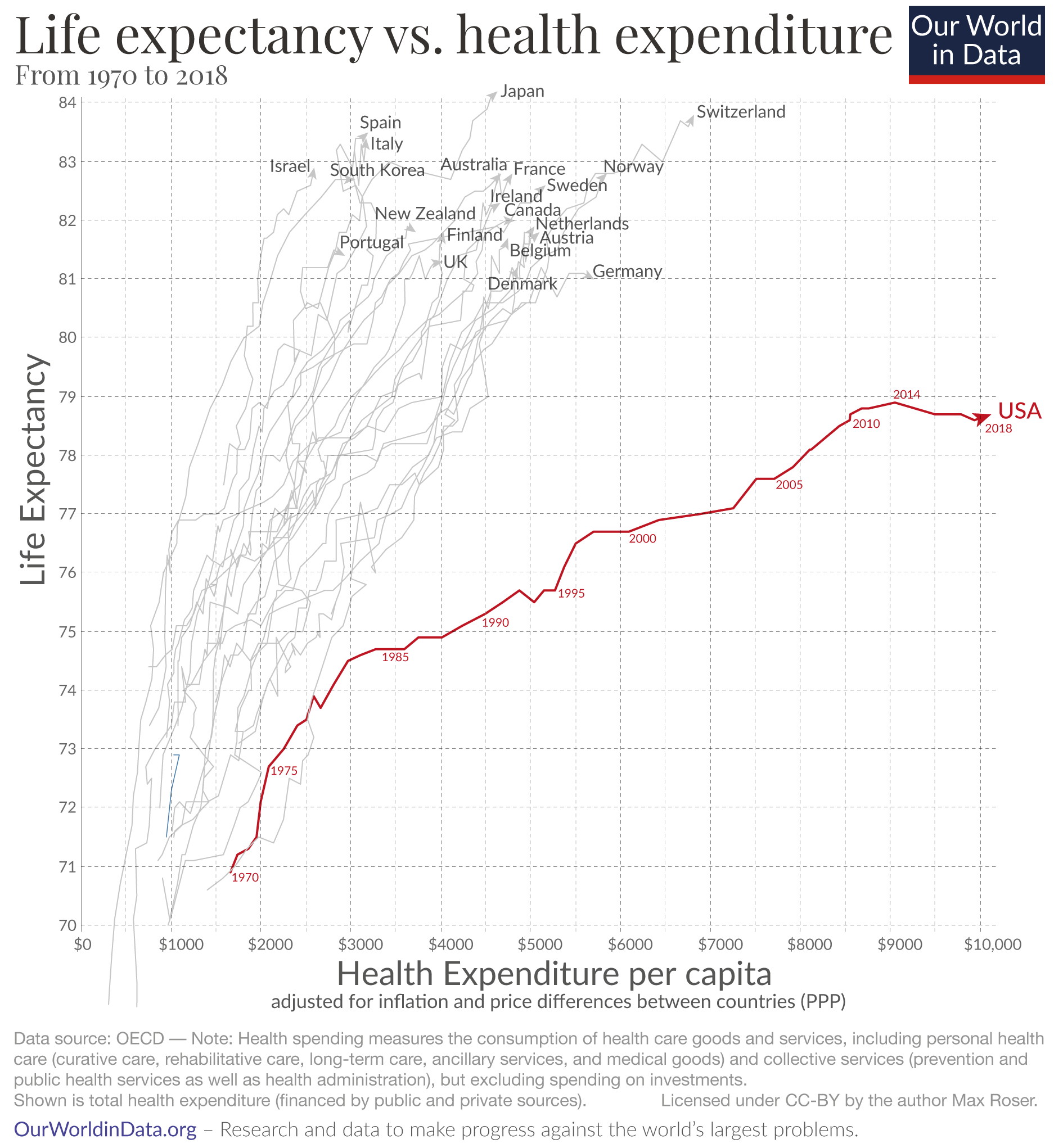



Why Is Life Expectancy In The Us Lower Than In Other Rich Countries Our World In Data



Why Do Some Countries Do Better Or Worse In Life Expectancy Relative To Income An Analysis Of Brazil Ethiopia And The United States Of America International Journal For Equity In Health




List Of Countries By Life Expectancy Wikipedia




Need And Channel Of Investment In Underdeveloped Countries Or Develop




Life Expectancy At Birth Female To Male Ratio Download Scientific Diagram




Life Expectancy In Low Income Countries On The Rise




Recent Trends In Life Expectancy Across High Income Countries Retrospective Observational Study The Bmj



1




Developing Countries Vs Developed Countries By Soren




Why Does Death Rate Go Up In More Developed Countries




Countries With Lowest Life Expectancy 19 Statista
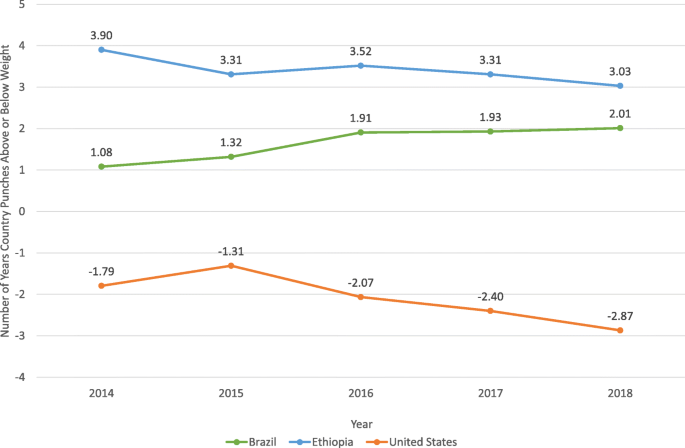



Why Do Some Countries Do Better Or Worse In Life Expectancy Relative To Income An Analysis Of Brazil Ethiopia And The United States Of America International Journal For Equity In Health



Life Expectancy




Longevity In Rich Countries The Economist




Pdf Factors Effecting Life Expectancy In Developed And Developing Countries Of The World An Approach To Available Literature




Life Expectancy Wikipedia




Comparison With Other Nations 16 Annual Report Ahr
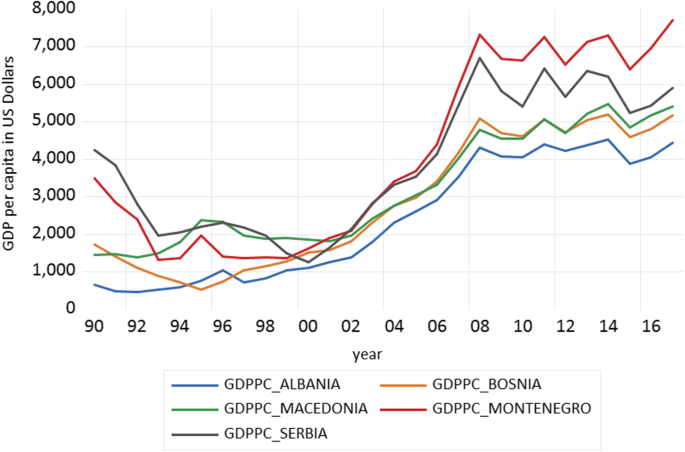



Socioeconomic Development And Life Expectancy Relationship Evidence From The Eu Accession Candidate Countries Genus Full Text



Developing Countries How To Improve Life Expectancy Life Expectancy



Life Expectancy Our World In Data




Low Life Expectancy In Developing Countries Essay In 21 Essay Developing Country Essay Writing




International Differences In Life Expectancy Gains And In Their Cost N Iussp
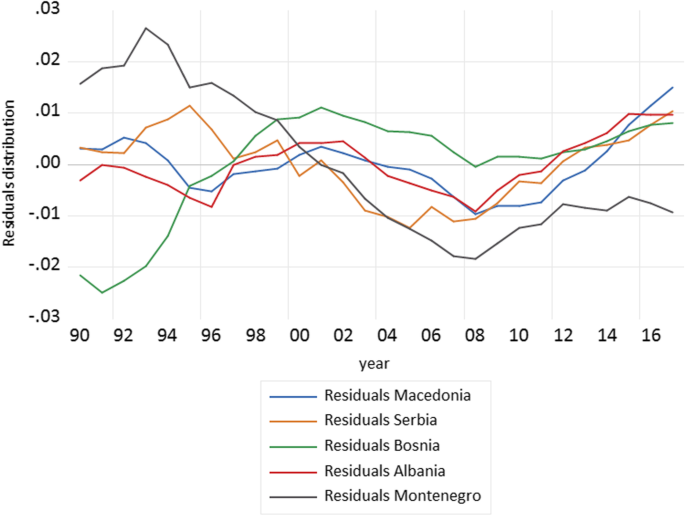



Socioeconomic Development And Life Expectancy Relationship Evidence From The Eu Accession Candidate Countries Genus Full Text




List Of Countries By Life Expectancy Wikipedia




Dynamics Of Life Expectancy And Life Span Equality Pnas




Declining Birthrate And Aging Population In Asia Educational Support To Low Income Households Improves Quality Of Labor Force And Productivity Discuss Japan




Life Expectancy An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Recent Trends In Life Expectancy Across High Income Countries Retrospective Observational Study The Bmj
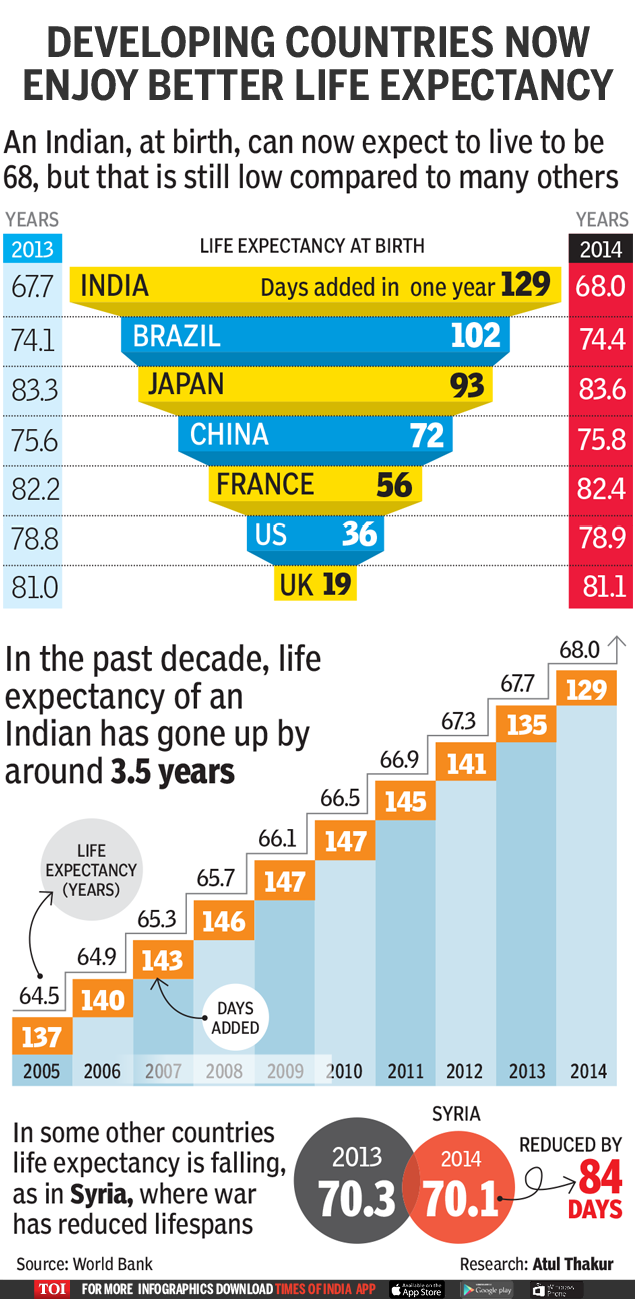



Infographic Average Indian Will Now Live For 3 5 More Years India News Times Of India
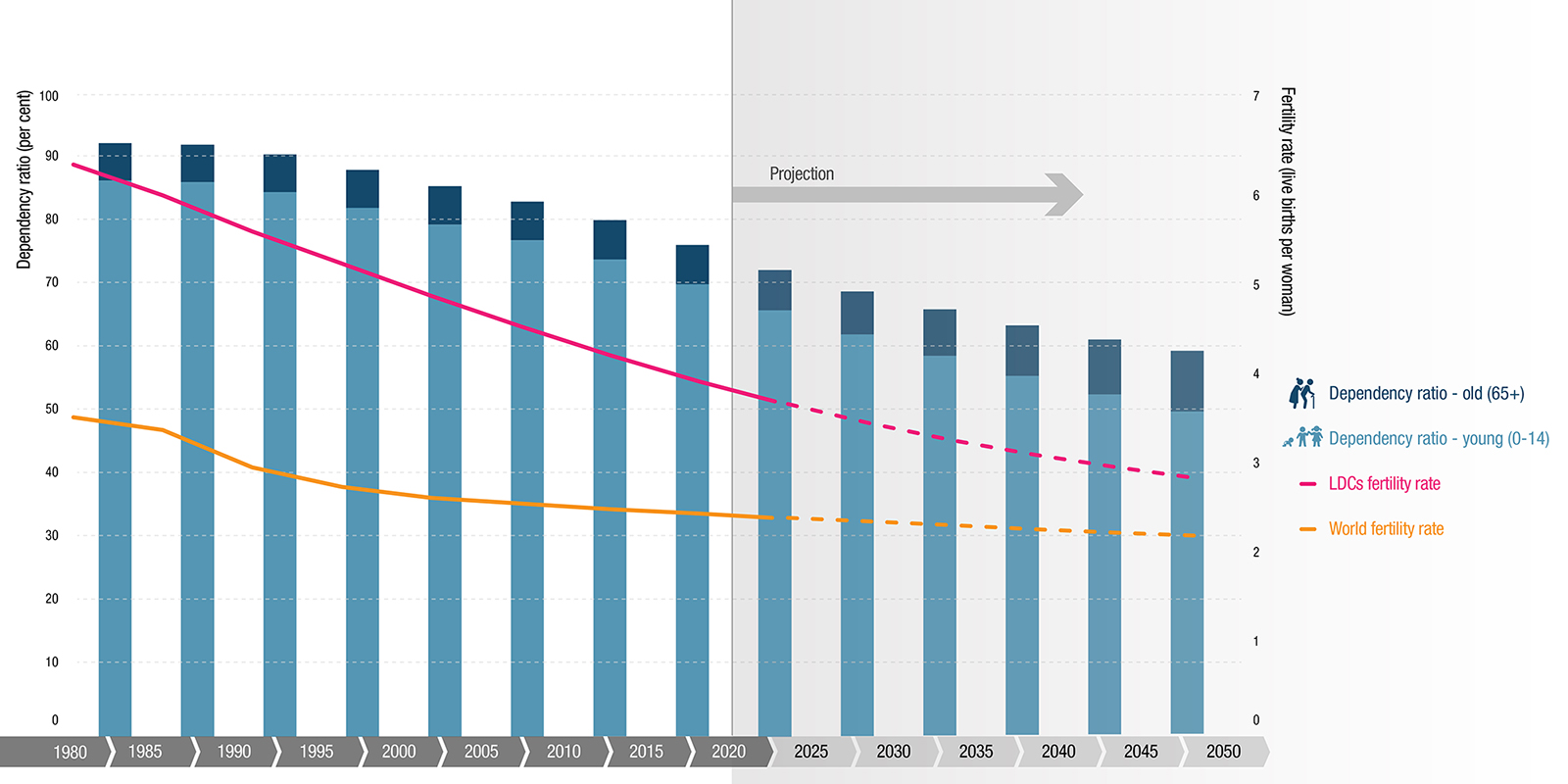



Harnessing Demographic Dividend In Least Developed Countries Unctad




Life Expectancy At Birth For The World And Development Groups 1950 2100 Download Scientific Diagram
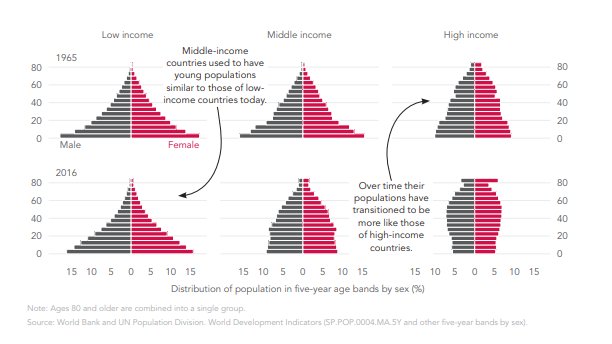



World Bank Pubs Dyk Low Income Countries Have Younger Populations Than High Income Countries Do As Countries Become Richer Fertility Rates Fall And Life Expectancy Rises T Co Owbmrwpgze Youth T Co R8jmndq2gt




Pdf Factors Effecting Life Expectancy In Developed And Developing Countries Of The World An Approach To Available Literature




Trial Exam Macro Part Development Economics 6012b0269y Uva Studeersnel
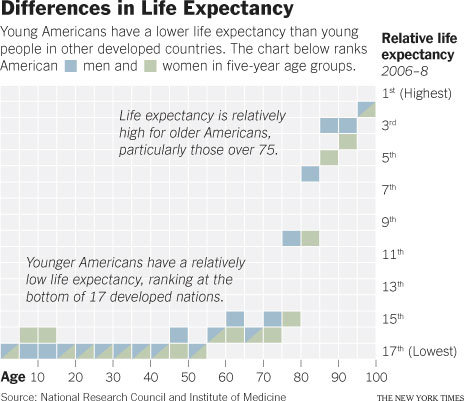



The U S 1 In Early Deaths Sociological Images




Causes For Low Life Expectancy How To Increase It E C




Difference Icj And Icc Pdf Developing Country International Criminal Court




Increasing But Insufficient Optimism About Future Life Expectancy




Human Development Indices And Indicators 18 Statistical Update World Reliefweb




What Is Happening To Life Expectancy In England The King S Fund




Dynamics Of Life Expectancy And Life Span Equality Pnas




List Of Countries By Human Development Index Wikipedia
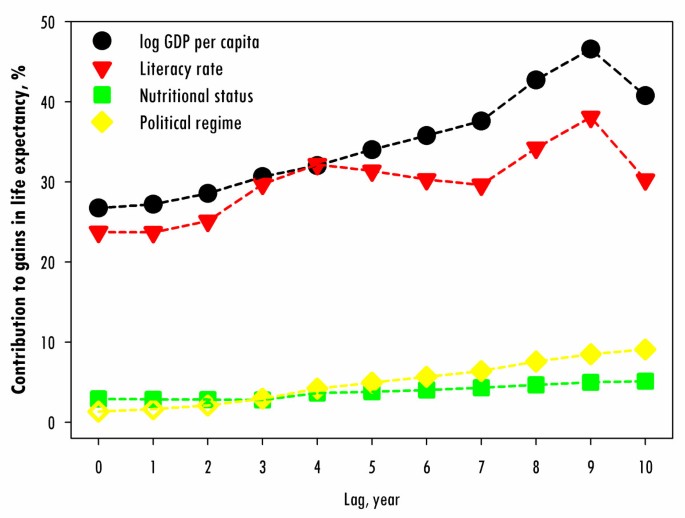



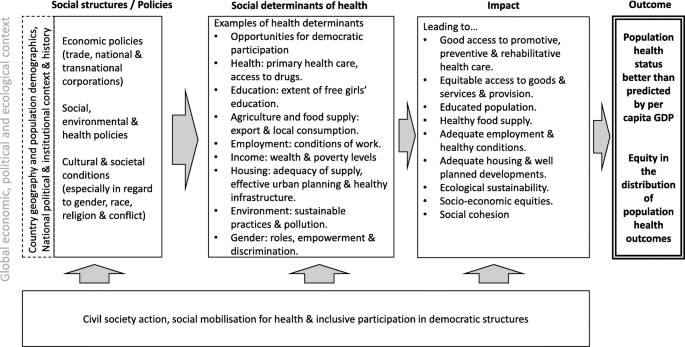
Political And Social Determinants Of Life Expectancy In Less Developed Countries A Longitudinal Study Bmc Public Health Full Text




Life Expectancy An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Reductions In Us Life Expectancy Due To Covid 19 And The Disproportionate Impact On The Black And Latino Populations Pnas



People In Hong Kong Have The Longest Life Expectancy In The World Some Possible Explanations National Academy Of Medicine




Health Care Around The World Global Issues



2



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿